
Carbon-11 is a synthetic isotope it is cyclotron-produced. This naturally-occurring isotope from cosmic ray bombardment may be used to date relics containing natural carbonaceous materials. It is widely used as a tracer in studying various aspects of metabolism. Carbon-14 is a beta emitter with a half-life of about 5,715 years. The process occurs when the unstable atomic nucleus of the radioisotope loses energy by emitting radiation. A radioisotope decays into other elements by a process called radioactive decay. Carbon-12 and Carbon-13 are stable isotopes. Carbon isotopes that occur naturally include Carbon-12, Carbon-13, and Carbon-14. Nevertheless, they display almost identical chemical properties. Therefore, they differ in atomic mass number. They have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons in their nuclei.

Isotopes refer to any of the two or more forms of the same element. Carbon-containing compounds may be classified as organic or inorganic. It may also interact with atoms or groups of atoms of different elements to form compounds. Carbon may interact with other carbon atoms and form allotropes. It has three naturally-occurring isotopes: Carbon-12, Carbon-13, and Carbon-14. From the discovery of Carbon-14 to radiocarbon dating of fossils, we can see what an essential role Carbon has played and continues to play in our lives today.Carbon is one of the most abundant elements on Earth. Although it may be seen as outdated, many labs still use Libby's half-life in order to stay consistent in publications and calculations within the laboratory. We now use what is known as the Cambridge half-life of 5730+/- 40 years for Carbon-14. Throughout the years, measurement tools have become more technologically advanced, allowing researchers to be more precise. From that point on, scientists have used these techniques to examine fossils, rocks, and ocean currents as well as to determine age and event timing. The accuracy of this proposal was proven by dating a piece of wood from an Ancient Egyptian barge, the age of which was already known.
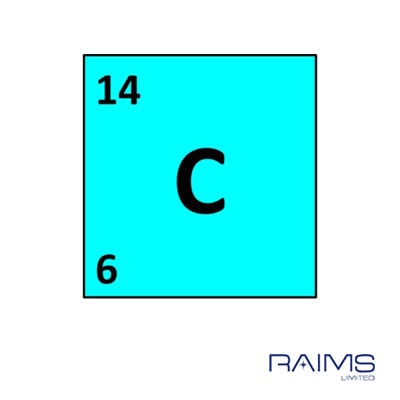
Using this hypothesis, the initial half-life he determined was 5568, give or take 30 years. Using this finding, Willard Libby and his team at the University of Chicago proposed that Carbon-14 was unstable and underwent a total of 14 disintegrations per minute per gram. They found a form, an isotope, of Carbon that contained 8 neutrons and 6 protons. In 1940, Martin Kamen and Sam Ruben at the University of California, Berkeley Radiation Laboratory did just that. Before Radiocarbon dating was discovered, someone had to find the existence of the 14C isotope.
DEFINE CARBON 14 SERIES
He demonstrated the accuracy of radiocarbon dating by accurately estimating the age of wood from a series of samples for which the age was known, including an ancient Egyptian royal barge dating from 1850 BCE. In 1960, Libby was awarded the Nobel Prize in chemistry for this work. Libby estimated that the steady-state radioactivity concentration of exchangeable carbon-14 would be about 14 disintegrations per minute (dpm) per gram. Emilio Segrè asserted in his autobiography that Enrico Fermi suggested the concept to Libby at a seminar in Chicago that year. The technique of radiocarbon dating was developed by Willard Libby and his colleagues at the University of Chicago in 1949.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
